Home / Science
Mitochondria and Neuroinflammation
Symbinas scientific team has found that the best way to prevent worsening in TBI is to focus on improving mitochondrial function and to inhibit neuro-inflammation to improve and preserve brain function in patients with TBI. These same mechanisms seem to be culprit in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s and ALS (Lou Gehrig’s disease).
Our drug candidates utilize novel methods for neuroenhancement (neurogenesis, axogenesis, synaptogenesis and neuroprotection) by improving mitochondrial function and decreasing neuroinflammation. The mitochondrial-targeted neuroenhancement treats the root cause and improves long term complications of concussion and TBI, such as anxiety, agitation, sleep disturbances, memory loss, cognitive decline, dementia and possibly impacts other neurodegenerative disorders as well including Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s Disease and even Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE).
Neurogenesis:
The observation that the human brain stem cells churns out new neurons throughout life is one of the biggest neuroscience discoveries of the past 20 years. Brain’s regenerative capacity can be harnessed to boost cognition or to treat injury or disease. The continued production of new neurons has been linked to improved learning and memory, and possibly even mood regulation.
Mitochondria In Cellular Regeneration And Neurogenesis:
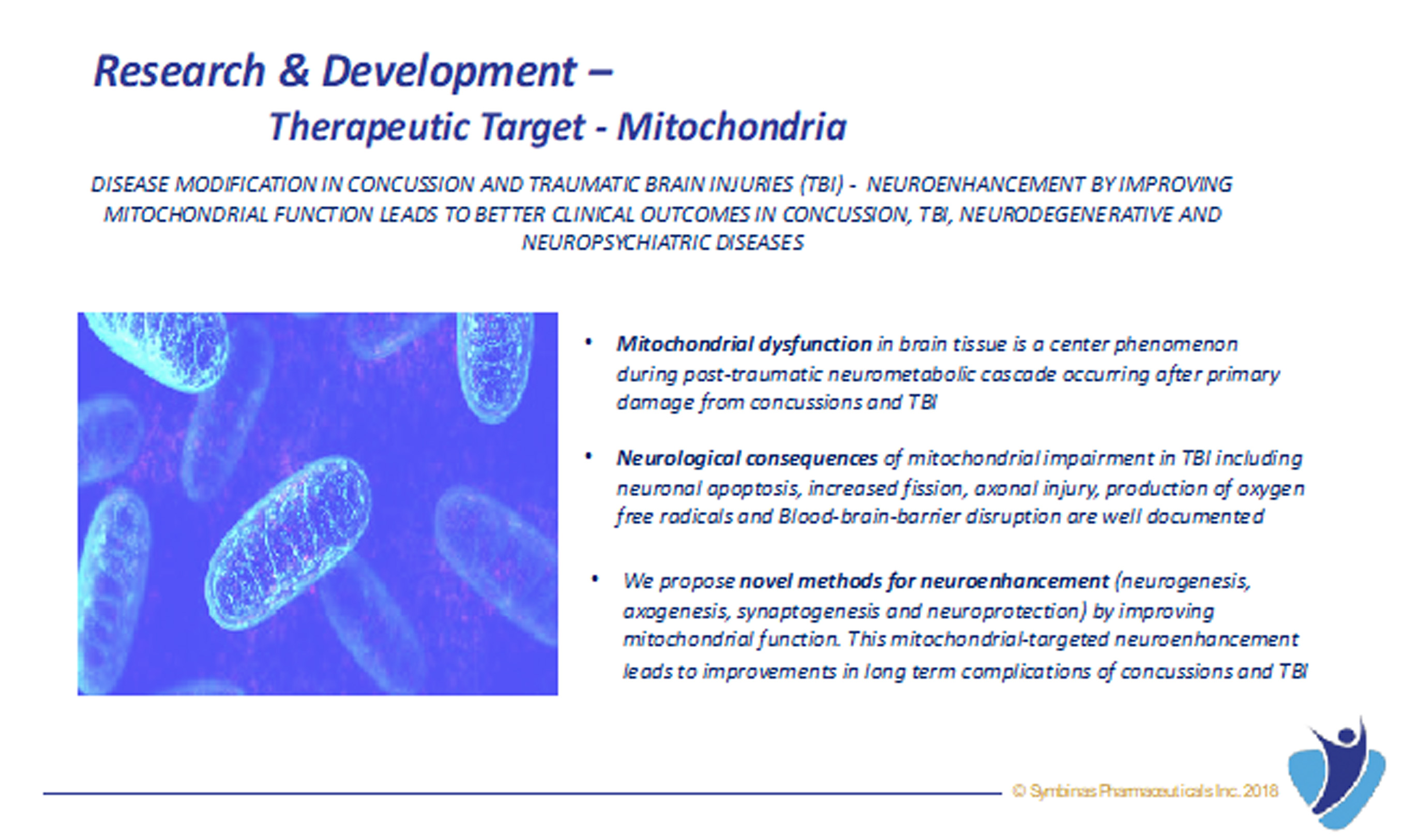
The role of mitochondria in cellular energy metabolism, cell signaling, and aging is well established. Mitochondrial dysfunction in cerebral tissue is now found to be a center phenomenon during post-traumatic neurometabolic cascade occurring after primary damage from concussion and TBI. Improving mitochondria in brain is the key pathway to improving brain function.
CONCUSSION & TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY
LEAD DRUG CANDIDATE SMB-603
Mitochondrial enhancement and stem cell stimulation by SMB-603 repairs the cellular damage seen in TBI.
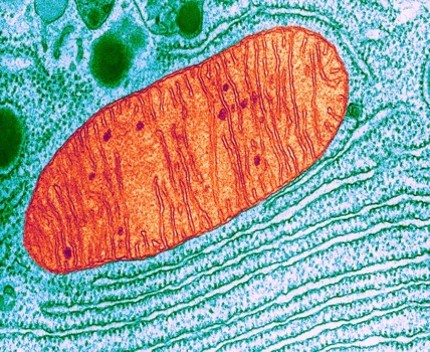
- Mitochondrial dysfunction in cerebral tissue is a central phenomenon during post-traumatic neurometabolic cascade occurring after primary damage from concussions and TBI
- The neurological consequences of mitochondrial impairment including neuronal apoptosis, increased fission, axonal injury, production of oxygen free radicals and Blood-brain-barrier disruption are well documented
- This mitochondrial-targeted neuroenhancement and neuroprotection leads to improvements in long-term complications of concussions and TBI.
- Studies show that small-molecule ingredient in SMB-603 improves the pathophysiological changes and symptoms seen in TBI, including cognitive, memory, emotional, motor and sensory symptoms
SCIENTIFIC DATA
SAFETY PROFILE:
- Safety well established in humans. In market for over 10 years with proven safety profile in human use globally. It has been marketed in dozens of countries around the world
ANIMAL EFFICACY DATA:
- Over 30 published studies showing strong animal efficacy data in TBI animal models
EFFICACY DATA IN HUMANS:
- Published reports with efficacy in patients with multiple psychiatric conditions
- Case report efficacy data obtained in patients with TBI using APIs in SMB-603 and SMB-710.

ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE & DEMENTIA
PROBLEM:
- Each Year $600 billion (worldwide) and $290 Billion (in U.S.) are spent on Alzheimer’s Disease and dementia
- 5.8 Million people in U.S. and 44 million people worldwide are living with Alzheimer’s Disease
- Not just memory loss – it is the 6th leading cause of death in U.S. Recent estimates indicate that the disorder may rank third as a cause of death for older people, just behind heart disease and cancer

SOLUTION:
- SMB-710 provides a multi-modal approach to treat Alzheimer’s disease
- Symbinas’ strategy provides innovative and rapid development of therapies to deliver lifesaving solutions in record time and minimum cost
- Existing Data – SMB-710 already has proven human safety and efficacy data and has been found to be effective in vivo models for receptor targets in Alzheimer’s disease
- Mode of Action – Stem Cell Stimulation with mitochondrial enhancement and Inhibiting Neuroinflammation
- Are being developed on an accelerated timeline at lower cost, lower risk and higher chance of success
COVID-19 PANDEMIC
PROBLEM:
- Key to decreasing morbidity and mortality is to urgently prevent and control respiratory tract infection
- Symbinas’ strategic approach presents the promise of enabling patient access to much-needed therapies sooner and at a lower cost, especially during this pandemic
SOLUTION:
- SMB-001 – Backed by proven scientific data, is being developed as an Intravenous formulation for faster and better effects in hospitalized COVID-19 patients (vs. other routes of delivery), thus decreasing morbidity and mortality in these patients
- Mode of Action – Immunomodulation
- Existing Data – It already has proven human safety data and has been found to be effective in human case treatments as well as in vivo models for receptor targets
- Symbinas’ strategy provides innovative and rapid development of therapies to deliver lifesaving solutions in record time at minimum cost, as is urgently needed for this pandemic
- With FDA’s special Coronavirus Treatment Accelerated Program (CTAP), 505(b)(2) pathway and Emergency Use Authorization (EUA), expected EUA from FDA to treat COVID-19 patients within 12 months*
Drug Candidate SMB-001
Immunomodulation by inhibiting NF-κB and cytokines, SMB-001 improves pathophysiological changes seen in respiratory and systemic disease in COVID-19 patients
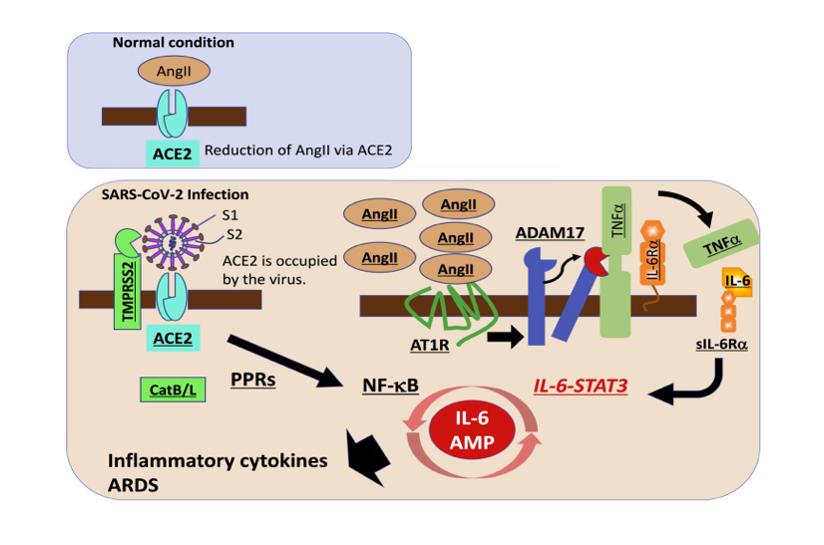
Possible therapeutic targets for COVID-19, a cytokine release syndrome.
SARS-CoV-2 uses angiotensin converting enzyme II (ACE2) and transmembrane serine protease 2 (TMPRSS2) as cell entry receptors, followed by a cytokine-related syndrome, ARDS, which is induced by the hyper-activation of the transcription factor NF-κB, most likely in nonimmune cells including lung epithelial cells, which describes enhanced NF-κB activation machinery via the coactivation of NF-κB and transcription factor STAT3. The molecules underlined indicate possible therapeutic targets for COVID-19, which is a cytokine release syndrome (CRS).
RE: Immunity. 2020 May 19; 52(5): 731–733. Published online 2020 April 22. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.04.003